I. Introduction
Importance of Oral Health
Oral health is a critical component of overall well-being. It goes beyond having a bright smile; good oral health is essential for proper nutrition, communication, and self-esteem. Neglecting oral health can lead to severe consequences, including infections, tooth loss, and systemic diseases. Among these potential issues, oral cancer stands out due to its life-threatening nature, emphasizing the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups.
Prevalence of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is a significant public health issue, affecting thousands of individuals globally each year. It encompasses cancers of the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses, and throat. The prevalence of oral cancer is alarming, with a higher incidence in populations exposed to known risk factors such as tobacco and alcohol use. Early detection through oral cancer screening is vital for improving survival rates and outcomes.
Significance of Oral Cancer Screening
Oral cancer screening is a critical preventive measure that can lead to early detection and treatment of oral cancer. Regular screening can identify precancerous conditions or early-stage cancer, significantly increasing the chances of successful treatment. Despite its importance, many people overlook the need for regular screenings, underscoring the necessity of raising awareness about oral cancer and the benefits of early detection.
II. Understanding Oral Cancer
Definition and Types of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer refers to cancerous growths in the mouth and surrounding areas. The most common type is squamous cell carcinoma, which originates in the flat cells lining the mouth and throat. Other types include minor salivary gland carcinomas and lymphomas, which are less common but still pose significant health risks.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for approximately 90% of all oral cancers. It typically develops on the lips, inside the mouth, on the back of the throat, and on the tonsils and salivary glands. This type of cancer is known for its aggressive nature and tendency to spread quickly, making early detection and treatment crucial.
Other Types of Oral Cancer
While squamous cell carcinoma is the most prevalent, other types of oral cancer include:
- Minor Salivary Gland Carcinomas: These cancers originate in the small salivary glands scattered throughout the lining of the mouth and throat.
- Lymphomas: These cancers arise from the lymphatic tissue in the base of the tongue and tonsils.
Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors for oral cancer is essential for prevention and early detection. The primary risk factors include:
- Tobacco Use: Both smoking and smokeless tobacco significantly increase the risk of developing oral cancer.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol use is another major risk factor, especially when combined with tobacco use.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): HPV, particularly HPV-16, is linked to a growing number of oral cancers, particularly in the oropharynx.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun increases the risk of lip cancer.
- Genetics: A family history of cancer can also elevate the risk of developing oral cancer.
III. The Importance of Oral Cancer Screening
Early Detection Saves Lives
Early detection of oral cancer through regular screenings can significantly improve survival rates. When identified early, the treatment for oral cancer is more effective, less invasive, and has a higher likelihood of success. Routine screenings can catch cancer before it progresses to advanced stages, which are more difficult to treat.
Oral Cancer Screening Methods
Various methods are used to screen for oral cancer, including:
- Visual Examination: Dentists and healthcare professionals look for abnormalities such as sores, red or white patches, and other unusual changes in the mouth.
- Physical Examination: This involves feeling the tissues in the mouth and throat for lumps or irregularities.
- Diagnostic Tests: If abnormalities are found, further tests such as biopsies, imaging tests, and laboratory tests may be conducted to diagnose the condition.
Frequency of Screening
Regular oral cancer screenings are essential, particularly for high-risk individuals. Recommendations for screening frequency vary:
- For Different Age Groups: Adults over 40 should have an annual screening, while younger individuals should be screened every three years.
- High-Risk Individuals: Those with significant risk factors, such as tobacco or alcohol use, should consider more frequent screenings.
IV. Warning Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Persistent Sores or Ulcers
One of the most common signs of oral cancer is a sore or ulcer in the mouth that does not heal within two weeks. These sores can be painful and may bleed easily.
Unexplained Bleeding
Unexplained bleeding in the mouth can be a sign of oral cancer. This symptom should not be ignored, especially if it occurs frequently.
Red or White Patches
Red or white patches on the gums, tongue, or lining of the mouth can be early indicators of oral cancer. These patches can be smooth or slightly raised and should be examined by a healthcare professional.
Difficulty Swallowing or Chewing
Oral cancer can cause pain or difficulty when swallowing or chewing. This symptom may also be accompanied by a persistent sore throat or the feeling that something is caught in the throat.
Persistent Sore Throat or Hoarseness
A sore throat or hoarseness that persists for an extended period can be a sign of oral cancer, particularly if it does not respond to typical treatments.
Numbness or Pain
Unexplained numbness or pain in the mouth, face, or neck should be evaluated as it can be a sign of oral cancer.
Lumps or Thickening of Tissue
The presence of lumps, thickened areas, or rough spots in the mouth can indicate oral cancer. These areas may be painful or tender.
Changes in Teeth or Dentures Fit
Oral cancer can cause noticeable changes in how teeth or dentures fit together, leading to discomfort and difficulty in speaking or chewing.
V. The Oral Cancer Screening Process
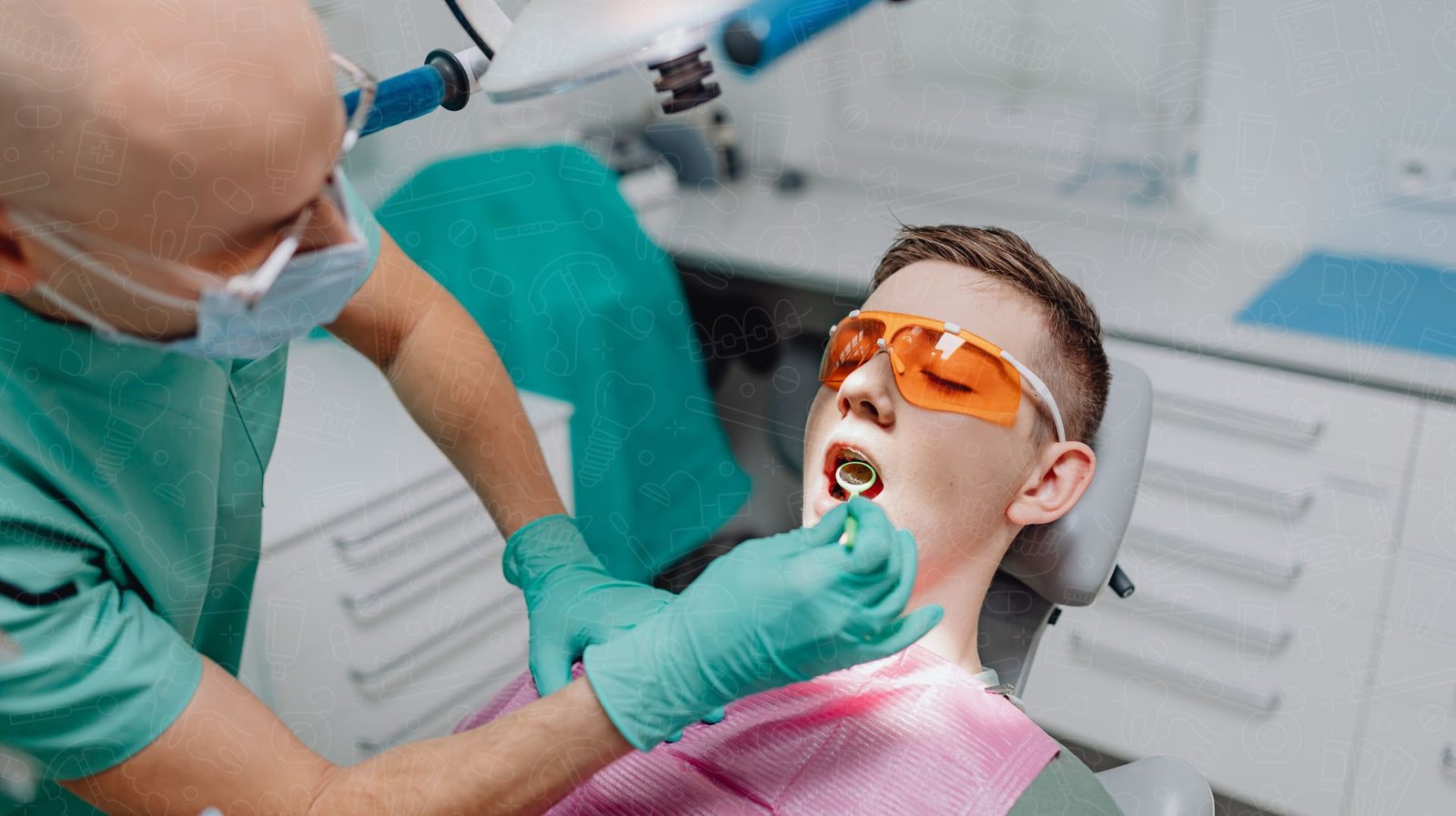
What to Expect During a Oral Cancer Screening
An oral cancer screening is a straightforward procedure that can be done during a routine dental visit.
Initial Consultation
The process begins with a discussion about the patient's medical history and any symptoms they may be experiencing.
Comprehensive Oral Examination
The dentist conducts a thorough examination of the mouth, looking for any abnormalities.
Use of Special Tools and Tests
Special tools, such as lights or dyes, may be used to highlight abnormal tissues that are not visible to the naked eye.
How Dentists and Hygienists Conduct Oral Cancer Screenings
Visual Inspection
Dentists visually inspect the mouth, lips, gums, tongue, and throat for signs of cancer.
Palpation of Head, Neck, and Oral Tissues
They also palpate (feel) the tissues in the mouth, neck, and head for any lumps or irregularities.
Use of Dye or Light for Better Detection
Special dyes or lights can help detect abnormal cells that might not be visible otherwise.
VI. Advances in Oral Cancer Screening
New Technologies and Techniques in Oral Cancer Screening
Recent advancements in technology have improved the accuracy and effectiveness of oral cancer screenings.
Fluorescence Visualization
This technique uses a special light to highlight abnormal tissues in the mouth, making it easier to detect early signs of oral cancer.
Brush Biopsy
A brush biopsy involves collecting cells from a suspicious area in the mouth for further examination under a microscope.
Saliva Testing, Non-invasive Oral Cancer Screening Option
Saliva tests can detect biomarkers associated with oral cancer, providing a non-invasive screening option.
Benefits of Advanced Oral Cancer Screening Methods
Increased Accuracy
Advanced screening methods can detect oral cancer at earlier stages with higher accuracy.
Non-Invasive Options
Many new techniques are non-invasive, making the screening process more comfortable for patients.
Early Stage Detection
These methods improve the chances of detecting oral cancer in its early stages, leading to better treatment outcomes.
VII. What to Do If You Notice Symptoms
Immediate Steps to Take
If you notice any symptoms of oral cancer, it is important to act quickly.
Contacting a Healthcare Professional
Schedule an appointment with a dentist or healthcare professional as soon as possible for a thorough evaluation.
Self-Examination Tips
Regular self-examinations can help you become familiar with your mouth and recognize any unusual changes early.
Importance of Professional Evaluation
Professional evaluation is crucial for diagnosing oral cancer and determining the appropriate course of action.
Possible Outcomes and Next Steps
Referral to a Specialist
If your dentist finds something suspicious, you may be referred to a specialist for further evaluation.
Further Diagnostic Testing
Additional tests, such as imaging scans or biopsies, may be required to confirm a diagnosis.
VIII. Preventive Measures to Reduce Oral Cancer Risk
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting healthy habits can significantly reduce your risk of developing oral cancer.
Quitting Tobacco
Eliminating tobacco use is one of the most effective ways to lower your risk.
Reducing Alcohol Consumption
Limiting alcohol intake can also help reduce your risk of oral cancer.
Healthy Diet
A diet rich in fruits and vegetables can boost your immune system and lower your cancer risk.
Safe Sun Practices
Using lip balm with SPF and avoiding excessive sun exposure can help prevent lip cancer.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
Routine dental visits play a crucial role in maintaining oral health and preventing oral cancer.
Role of Routine Dental Visits in Prevention
Regular check-ups allow for early detection of any abnormalities and professional cleanings help maintain overall oral health.
Professional Cleanings and Examinations
Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup that can lead to oral health issues, and thorough examinations can catch early signs of cancer.
Vaccination for HPV
Getting vaccinated against HPV can reduce the risk of HPV-related oral cancers.
IX. Conclusion
Regular oral cancer screenings are essential for early detection and successful treatment. Understanding the warning signs, risk factors, and screening process can help prevent oral cancer or catch it early when it is most treatable.
Importance of Awareness and Screening
Increasing awareness about oral cancer and the importance of screenings can save lives.
Recognizing Warning Signs of Oral Cancer Screening
Being aware of the warning signs and seeking prompt medical attention can lead to early diagnosis and better outcomes.
Taking Preventive Measures
Adopting a healthy lifestyle and maintaining regular dental visits are key preventive measures.
Final Thoughts
Prioritizing oral health through regular oral cancer screenings and preventive measures is crucial for reducing the risk of oral cancer.
Taking care of your oral health should be a priority, and regular oral cancer screenings are an essential part of that care.
Regular screenings can detect oral cancer early, leading to more effective treatment and better chances of survival.