Introduction to Gum Disease Prevention
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, constitutes a significant concern for oral health, affecting millions worldwide. It typically begins with gingivitis—a mild form of gum disease characterized by inflammation and irritation of the gums. If not addressed, it can escalate to periodontitis, which affects the supporting structures of the teeth, leading to potential tooth loss and other serious health complications. Recent studies have even linked untreated gum disease to conditions like heart disease and diabetes, underscoring the importance of preventive care.
The impact of gum health extends beyond the mouth. Poor gum health can introduce harmful bacteria into the bloodstream, contributing to systemic issues. Recognizing the symptoms early—such as bleeding gums and persistent bad breath—can facilitate timely intervention. Gum disease prevention strategies, including consistent oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing, play a fundamental role in mitigating the risks associated with gum disease. Regular visits to a dental professional can also provide critical assessments and cleanings that remove plaque buildup.
In a world where overall health is increasingly connected to oral well-being, understanding gum disease and the importance of preventive measures is essential for maintaining a healthy smile throughout life. This article explores the fundamentals of gum disease, outlines effective prevention methods, and highlights the role of diet and dental checkups in promoting robust gum health.
What Is Gum Disease and Why Prevention Matters
Gum disease, clinically known as periodontal disease, is a prevalent oral health issue affecting a significant portion of the population. It progresses through several stages, starting with gingivitis, characterized by inflammation and irritation of the gums, and potentially advancing to periodontitis, where the supporting structures of the teeth are compromised. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and has been linked to serious health conditions, such as heart disease and diabetes.
Understanding the importance of gum health is crucial for overall well-being. The bacteria that accumulate in plaque can cause inflammation, leading to discomfort and advanced periodontal issues. Prevention plays a vital role in maintaining gum health, as early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications. Regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings are foundational practices that help to remove plaque and prevent gum disease from developing.
Moreover, individual risk factors, including genetics and lifestyle choices, can influence susceptibility to gum issues. Therefore, being proactive about oral hygiene and incorporating preventive measures are essential in mitigating the long-term consequences that may arise from neglecting gum health. Establishing strong habits and understanding the significance of gum health forms the basis for a lifetime of oral wellness.
Daily Oral Hygiene Habits for Gum Disease Prevention
Maintaining effective daily oral hygiene is crucial in gum disease prevention. Gum disease, often a silent condition, can progress from gingivitis to more severe stages if proper care is neglected. Daily habits should include brushing teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste. This not only helps remove food particles but also reduces bacterial plaque buildup, a primary contributor to gum inflammation.
Flossing is an equally important routine that cannot be overlooked. It eliminates debris and plaque between teeth where toothbrushes cannot reach, which is vital for maintaining healthy gums. It is recommended to floss at least once daily, preferably before brushing, to enhance the effectiveness of the oral hygiene routine.
Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can further support gum health. Mouthwash aids in reducing bacteria in the mouth and freshens breath. For optimal results, choose a mouthwash that specifically targets gum disease.
In addition to these practices, individuals are encouraged to adopt regular routines and stay consistent. Utilizing the right tools, such as soft-bristled toothbrushes and dental devices, ensures that the mouth remains clean without damaging delicate gum tissue. By integrating these daily habits, individuals can substantially lower their risk of developing gum disease and promote long-lasting gum health.
The Role of Diet and Nutrition in Preventing Gum Disease
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health and gum disease prevention. Nutrient-rich foods contribute to the body's immune response, which is essential for combating inflammation and infection in the gums. Key vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, calcium, and antioxidants, are particularly beneficial for gum health.
Vitamin C, found in fruits like oranges and strawberries, aids in tissue repair and reduces the risk of periodontal issues. Calcium, present in dairy products and leafy greens, strengthens the bone structure surrounding teeth, further protecting them from decay. Antioxidants, abundant in foods like berries and nuts, can help reduce inflammation and promote overall gum health.
Additionally, a diet low in sugar is vital for preventing the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth. Sugary foods and beverages create an acidic environment that can lead to plaque buildup, increasing the likelihood of gum disease. Incorporating whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables not only supports gum health but also contributes to overall well-being.
In summary, maintaining a diet rich in essential nutrients while minimizing sugar intake can significantly reduce the risk of gum inflammation and infection. Individuals aiming to enhance their oral health should consider the direct impact of nutrition on their gums as part of a comprehensive preventive strategy against gum disease.
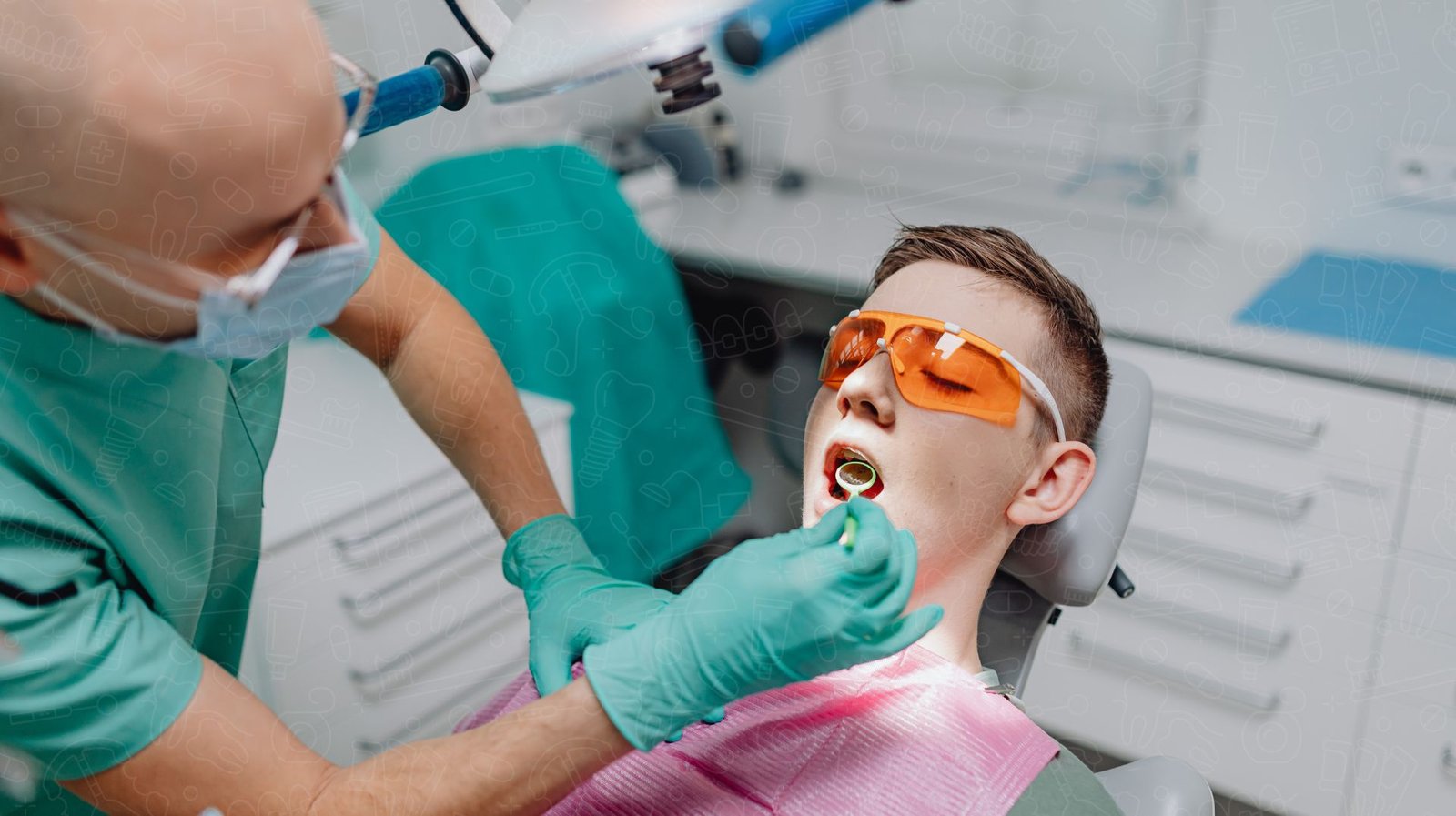
Importance of Regular Dental Checkups for Gum Health
Regular dental checkups play a crucial role in maintaining gum health and gum disease prevention. These visits typically include professional cleanings that remove plaque and tartar, which everyday brushing and flossing may miss. Dentists can identify early signs of gum disease during these appointments, allowing for timely intervention before more serious issues develop.
The frequency of dental visits is often recommended to be every six months, though some individuals may need more frequent assessments based on their dental health or risk factors. During these checkups, dental professionals also provide personalized advice on maintaining optimal oral hygiene practices, reinforcing the importance of techniques and habits that support gum health.
Additionally, professional evaluations help monitor any existing conditions that could impact gum health, such as diabetes or hormonal changes. Early detection of gum issues not only leads to effective treatment but can also prevent complications such as tooth loss and systemic health concerns associated with advanced gum disease.
In summary, committing to regular dental checkups is pivotal for sustaining healthy gums. By ensuring consistent professional oversight, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of gum disease and foster an environment for lasting oral health.
Risk Factors That Increase the Chances of Gum Disease
Gum disease, a common oral health issue, can be exacerbated by several risk factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for prevention and maintaining optimal gum health. Smoking is one of the leading contributors; it compromises blood flow to the gums, impairing healing and increasing susceptibility to infections. Individuals with diabetes also face heightened risks, as this condition can lead to increased blood sugar levels that may exacerbate gum inflammation and disease.
Hormonal changes, particularly in women during pregnancy or menopause, can make gums more sensitive and vulnerable to disease. Poor nutrition, including a lack of essential vitamins like Vitamin C, can weaken gum tissue and reduce the body’s ability to fend off infections. Additionally, individuals with a family history of gum disease may have a genetic predisposition that warrants extra vigilance.
Certain medical conditions, including autoimmune diseases, further complicate gum health by disrupting the body’s natural defenses. Medications that cause dry mouth can also contribute to gum disease, as a lack of saliva can lead to increased plaque buildup and bacterial growth.
By identifying these risk factors, individuals can take proactive measures to protect their gum health. Implementing comprehensive oral hygiene practices, maintaining a balanced diet, and regularly consulting with a dental professional can significantly enhance gum disease prevention efforts. Understanding the complex interplay of these factors empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their oral health.
Early Signs of Gum Disease and When to Seek Help
Recognizing the early signs of gum disease is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health. Initial symptoms often include subtle indicators such as bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing, and persistent bad breath that does not improve with regular oral hygiene. Other signs may include swollen or tender gums, receding gum lines, and changes in bite alignment or the fit of dentures.
Individuals should not ignore these symptoms, as they can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, including periodontal disease, which has been linked to systemic health issues such as heart disease and diabetes. Early intervention can significantly improve treatment outcomes and prevent further complications.
It is advisable for individuals experiencing any of these symptoms to seek professional dental advice promptly. Dentists can perform a thorough examination to diagnose the issue accurately and recommend appropriate interventions. Regular dental checkups play a vital role in early detection, allowing for the implementation of preventive measures tailored to individual needs. By noting these early signs and addressing them quickly, individuals can take proactive steps towards ensuring their gum health and advancement of gum disease prevention. Prioritizing regular dental visits and maintaining vigilance over oral symptoms will contribute to long-term periodontal health.
Conclusion: The Importance of Gum Disease Prevention
In summary, understanding gum disease and its prevention is vital for maintaining overall oral health. With its onset often marked by gingivitis, individuals must recognize the symptoms early to prevent progression to more severe stages, such as periodontitis. Incorporating effective daily oral hygiene practices—brushing, flossing, and utilizing antimicrobial mouthwash—can significantly mitigate the risk of developing gum disease. Additionally, a nutrient-rich diet and regular dental checkups emerge as essential strategies to promote healthy gums and manage any potential risks associated with factors such as smoking or diabetes.
The health of the gums has far-reaching implications beyond the mouth, impacting systemic health. By highlighting the connections between gum health and conditions like heart disease, this article underscores the crucial nature of prevention. Readers are encouraged to stay informed about the signs of gum disease and engage in proactive measures, reinforcing the importance of oral hygiene and routine dental visits. Overall, fostering awareness and understanding of gum disease prevention empowers individuals to take charge of their oral health, ensuring their smiles remain healthy and vibrant throughout life.