Introduction
Tooth decay, a common yet preventable dental issue, poses a significant risk to overall oral health. It is primarily caused by the interactions of bacteria with food particles, particularly sugars, leading to the gradual breakdown of tooth structure. Understanding the process of tooth decay—how it begins with the formation of plaque and evolves into more complex dental problems—is vital for anyone looking to maintain their dental health. The early signs of decay, such as white spots on enamel and sensitivity to temperature changes, often go unnoticed until the damage progresses further, necessitating professional intervention.
This article provides an in-depth exploration of tooth decay, focusing on its development, identifying early signs, and recognizing risk factors, which include dietary habits, oral hygiene practices, and genetic predispositions. Additionally, readers will discover essential strategies for detecting decay during daily oral care, the importance of routine dental visits, and effective prevention tips to halt the progression of early decay.
By increasing awareness of tooth decay's intricacies, individuals can take proactive measures to safeguard their teeth and ensure long-lasting oral health. This knowledge empowers readers to enhance their dental hygiene, making informed choices that help keep their smiles bright and healthy. Join us as we delve into the intricate world of tooth decay and uncover how to effectively combat this prevalent dental concern.
What Is Tooth Decay and How Does It Develop?
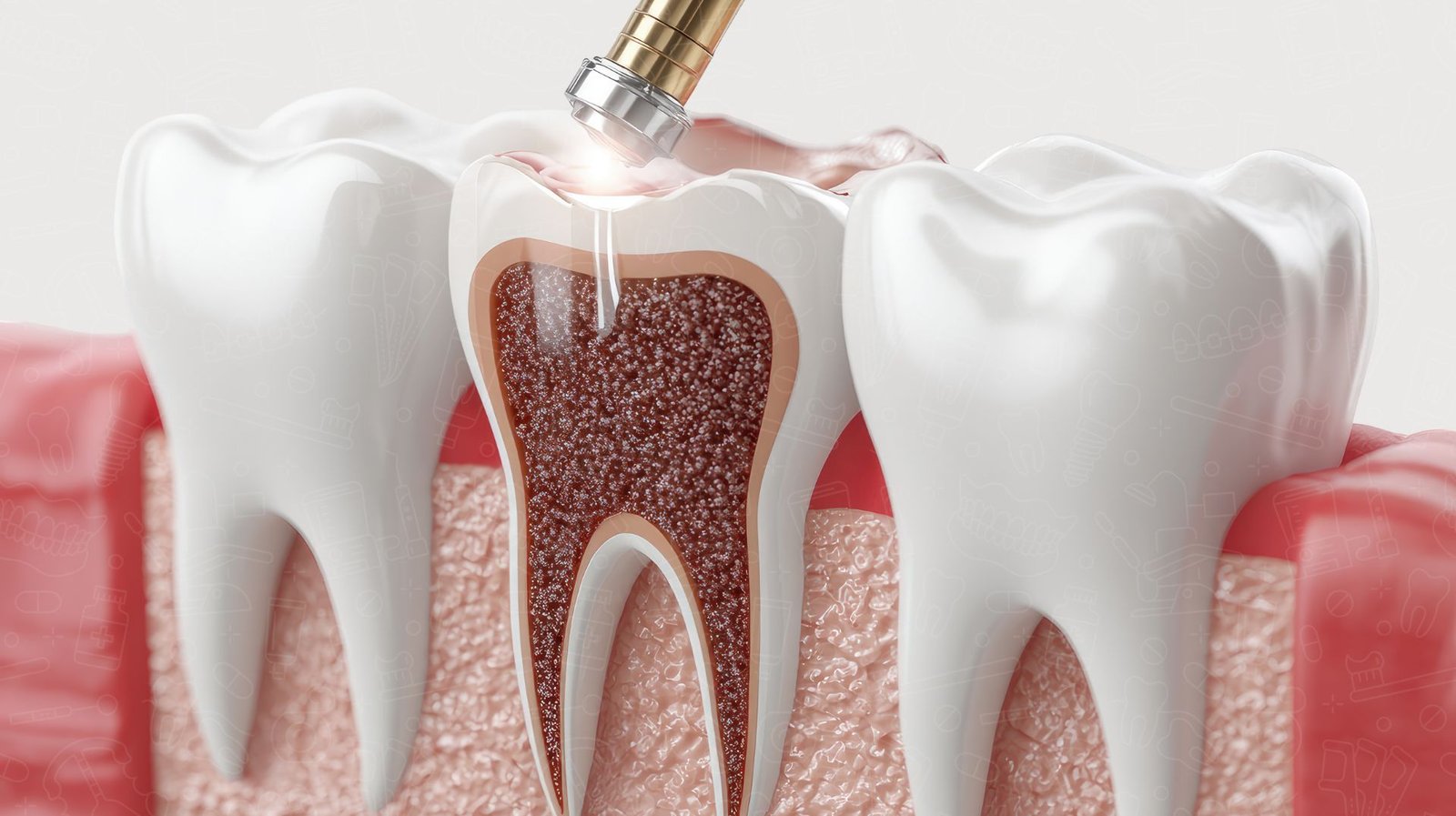
Tooth decay, also referred to as dental caries, is a progressive damage to the structure of the tooth, primarily caused by the activity of bacteria and their byproducts. The process begins with the formation of plaque, a sticky film that accumulates on teeth due to food particles, sugars, and saliva. When oral hygiene is inadequate, bacteria in plaque convert sugars into acids, leading to the demineralization of enamel, the hard outer layer of the tooth.
Over time, repeated acid attacks weaken the enamel, leading to the formation of cavities. Initially, the enamel may develop white spots, a sign of mineral loss, before progressing to more extensive damage that requires professional treatment. Factors such as diet, particularly high sugar content, and low oral hygiene practices, speed up this process. Additionally, certain individuals may have a genetic predisposition that increases their risk for tooth decay, making regular dental care vital.
Awareness of how tooth decay develops is essential for individuals aiming to maintain oral health. By understanding the roles that plaque, bacteria, and acids play in this process, individuals can take preventative measures to protect their teeth, such as maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental visits. This knowledge contributes significantly to avoiding the complications associated with untreated decay.
Common Early Signs of Tooth Decay to Watch For
Tooth decay can begin subtly, making it essential to be aware of its early signs. One of the first indicators is the appearance of white spots on the teeth. These spots occur when minerals are lost from the enamel, signaling initial demineralization. Another symptom to monitor is increased tooth sensitivity. Individuals may notice discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sugary foods, which suggests that the enamel is weakened.
Additionally, mild pain in the affected area can develop as decay progresses. This discomfort may not be constant but can become more pronounced over time, indicating that the decay process is advancing and that intervention may be necessary. Changes in taste or a persistent bad breath can also accompany early tooth decay.
It is crucial to recognize these warning signs promptly, as addressing them early can prevent more severe dental issues. Regular self-examination during daily oral hygiene routines can help individuals identify these symptoms sooner rather than later. Staying vigilant and proactive about oral health is vital for maintaining strong teeth and preventing the progressive nature of decay. Through awareness and prompt action, individuals can safeguard their dental health from the advancements of tooth decay.
Risk Factors That Increase the Chance of Early Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is a prevalent dental concern, influenced by various risk factors that can enhance its development. Individuals with poor dietary habits, particularly those high in sugars and acids, are at increased risk for early tooth decay. Consuming sugary snacks and beverages provides fuel for cavity-causing bacteria, leading to the production of harmful acids that erode enamel over time.
Additionally, inadequate oral hygiene practices contribute significantly to the risk of decay. Neglecting to brush and floss regularly allows plaque to accumulate, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth. Those who skip routine dental care and fail to maintain consistent brushing and flossing routines are more vulnerable to the onset of decay.
Genetic factors also play a crucial role in an individual’s susceptibility to tooth decay. Certain genetic predispositions can lead to weaker enamel, making teeth more prone to decay. Moreover, conditions like dry mouth, often linked to medications or health issues, can further elevate the risk, as saliva plays a vital role in neutralizing acids and protecting teeth.
By understanding these risk factors—diet, hygiene practices, and genetic predispositions—individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate their risk of early tooth decay, thus safeguarding their oral health. Addressing these concerns is essential for maintaining healthy teeth and preventing decay complications in the future.
How to Detect Early Tooth Decay During Daily Oral Care
Detecting early tooth decay during daily oral care is crucial for maintaining dental health. Regular brushing and flossing not only help remove food particles and plaque but also provide an opportunity to identify potential issues. Individuals should be vigilant for subtle changes in their teeth while performing their oral hygiene routine.
When brushing, it is beneficial to examine the surfaces of the teeth closely. Look for discolored areas, especially white spots, which may indicate early demineralization. These spots can be a precursor to cavities and should prompt further investigation. Additionally, sensitivity to hot or cold foods can signal enamel erosion, a common sign of starting tooth decay.
While flossing, one should pay attention to any unusual sensations or discomfort between the teeth. Areas that bleed during flossing may suggest gum issues or early decay that necessitate dental attention. The texture of the floss can also provide clues; if it feels gritty or catches unexpectedly, this could be another sign of decay.
Incorporating these observations into daily oral care routines enhances the ability to detect early decay. By identifying symptoms during home care, individuals can take proactive steps to consult a dental professional for further evaluation and treatment. Staying informed about these signs ensures that minor issues are addressed promptly, contributing to long-term oral health.
The Role of Regular Dental Visits in Identifying Early Decay
Regular dental visits play a crucial role in the early detection and management of tooth decay. These checkups allow dental professionals to examine teeth and gums closely, identifying early signs of decay that may not be noticeable at home. During these visits, dentists can utilize advanced diagnostic tools, such as digital X-rays, to pinpoint decay beneath the enamel layer, preventing potential complications.
Routine dental examinations typically occur every six months, giving patients an opportunity for professional cleaning, which removes plaque and tartar that contribute to decay. Regular checkups also enable dentists to provide personalized feedback on oral hygiene practices, helping individuals understand the specific risks they may face.
Furthermore, dental professionals can apply preventive measures, such as fluoride treatments and sealants, which can fortify tooth enamel against decay. This proactive approach not only helps in identifying early tooth decay but also educates patients on maintaining oral health, reducing the likelihood of advanced treatments in the future.
In summary, regular dental visits serve as an essential component in oral care, allowing for early detection and intervention of tooth decay, ultimately safeguarding long-term dental health. By prioritizing these appointments, individuals can take significant strides toward preventing decay before it progresses and causes irreversible damage.
Prevention Tips to Stop Early Signs of Tooth Decay from Progressing
To effectively prevent early tooth decay from worsening, individuals can adopt a multifaceted approach focusing on diet, oral hygiene practices, and the use of fluoride. A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly those critical for dental health like calcium and vitamin D, can help strengthen tooth enamel. Reducing the intake of sugary and acidic foods is essential, as these can lead to the formation of plaque, which eventually causes decay.
Maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine is fundamental. Brushing teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste helps remineralize enamel and protect against decay. Additionally, daily flossing is crucial for removing plaque and food particles from between the teeth, areas often overlooked. Using mouthwash that contains fluoride can provide extra protection and promote overall oral health.
Regular consumption of fluoride, whether through toothpaste or professional dental treatments, plays a significant role in tooth decay prevention. Fluoride not only strengthens existing enamel but also assists in repairing early signs of decay.
Moreover, staying hydrated and utilizing products that recall moisture in the mouth, such as sugar-free gum, can contribute to a healthier oral environment. Incorporating these preventative measures into daily routines may significantly reduce the risk of tooth decay and promote long-term dental health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding tooth decay is pivotal for maintaining optimal oral health and preventing serious dental issues. This article has explored the intricacies of tooth decay, detailing its development stages, early signs to watch for, and the various risk factors that can exacerbate the problem. By highlighting the importance of conscious dietary choices, diligent oral hygiene practices, and regular dental visits, individuals are empowered to combat this prevalent condition effectively.
Taking proactive measures—such as recognizing early warning signs, maintaining a balanced diet, and utilizing fluoride treatments—can significantly reduce the likelihood of tooth decay progression. Routine checkups with dental professionals not only aid in early detection but also reinforce the importance of preventive care, further safeguarding oral health.
As individuals integrate these strategies into their daily routines, they will be better equipped to protect their teeth from the damaging effects of decay. By prioritizing awareness and action, maintaining strong dental health becomes an achievable goal. Ultimately, this comprehensive understanding of tooth decay serves as a valuable guide for fostering brighter, healthier smiles for years to come.