Introduction
Dental cavities are small holes in teeth caused by decay, often leading to pain, sensitivity, and infection if left untreated. Timely intervention is essential to preserve natural tooth structure and prevent more invasive procedures. Dental fillings for cavity treatment play a crucial role in restoring the tooth’s shape, function, and integrity after decay removal. These fillings seal the cavity, stopping further damage and discomfort. Various materials are available, each with unique benefits—such as amalgam, composite resin, ceramic, glass ionomer, and gold. Understanding these options helps patients make informed choices for their oral health.
What Are Dental Fillings?
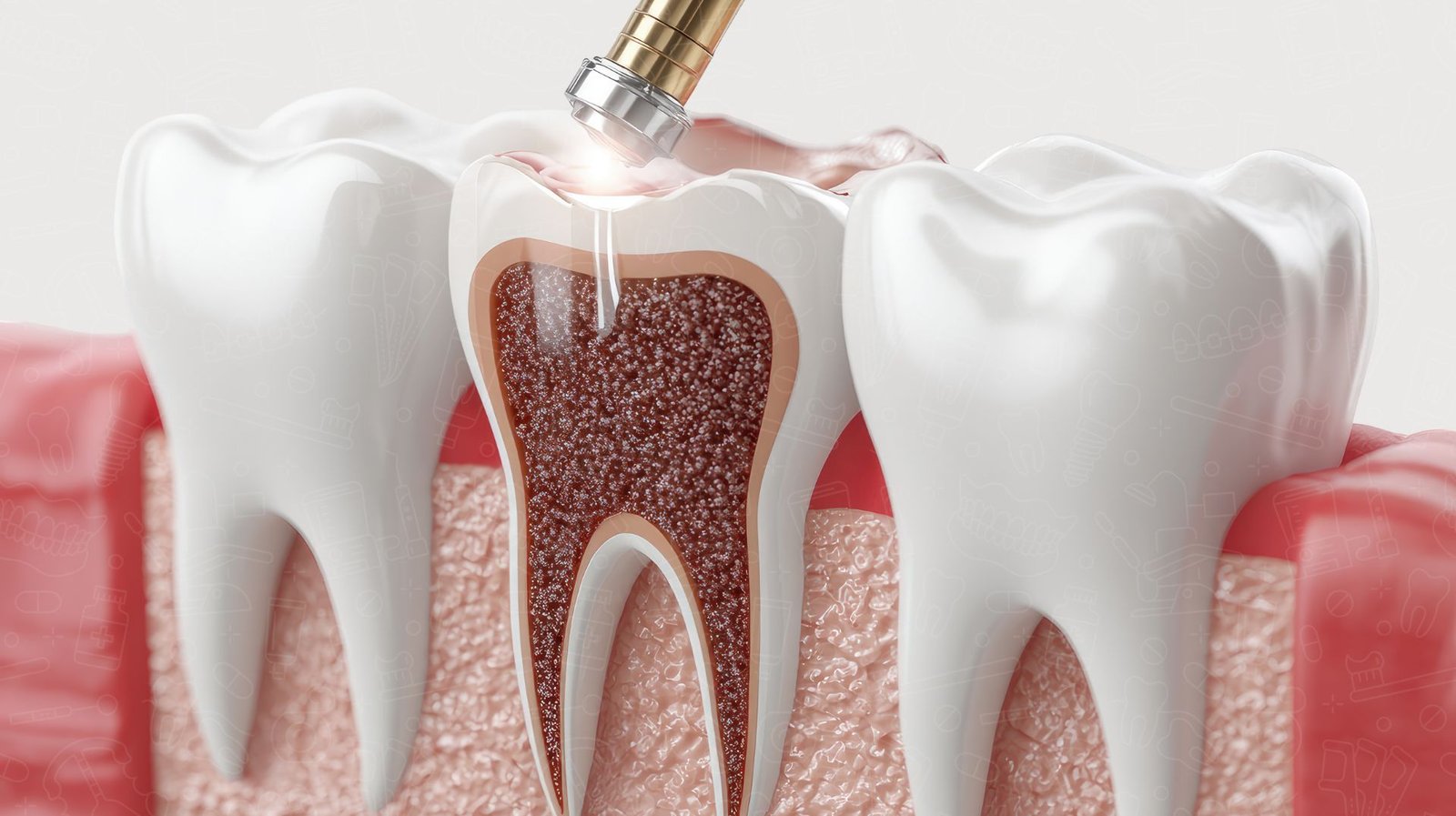
Dental fillings for cavity treatment are restorative materials used to repair teeth damaged by decay. When plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, accumulates on teeth and interacts with sugars from food, it produces acids that erode the enamel. Over time, this leads to cavities—permanent holes in the tooth structure. If untreated, cavities can progress deeper, affecting the tooth pulp and causing pain, infection, or even tooth loss.
Dental fillings are essential because they halt the spread of decay and restore the tooth’s normal function and appearance. They prevent further damage, maintain structural integrity, and protect against sensitivity or bacterial invasion.
The procedure for dental fillings for cavity treatment typically involves numbing the area, removing the decayed portion of the tooth with a dental drill or laser, and thoroughly cleaning the cavity. The dentist then fills the space with a suitable filling material, such as composite resin, amalgam, ceramic, or glass ionomer, shaping and polishing it for a smooth finish. This treatment is quick, effective, and crucial in maintaining long-term oral health. Choosing the right filling material depends on several factors, including the cavity’s size and location, durability needs, and cosmetic preferences.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Filling Material
When selecting the right material for dental fillings for cavity treatment, several important factors influence the decision. One of the primary considerations is the size and location of the cavity. Cavities on chewing surfaces or back teeth require stronger, more durable materials like amalgam or gold, while front teeth benefit from tooth-colored options like composite resin or ceramic for a natural appearance.
Durability and longevity are also crucial. While amalgam and gold fillings are known for lasting 10–15 years or more, composite and glass ionomer fillings may have a shorter lifespan, especially in high-pressure areas. Choosing a filling that withstands daily wear is vital for long-term oral health.
Aesthetic preferences play a major role, particularly for visible areas. Patients often prefer composite resin or ceramic for their ability to blend seamlessly with natural teeth. However, these may come at a higher cost.
Speaking of cost, financial considerations and insurance coverage can greatly affect the choice. Amalgam is typically more affordable and widely covered by dental plans, while gold and ceramic options may involve higher out-of-pocket expenses.
Lastly, allergies or sensitivities must be taken into account. Some individuals may react to metals in amalgam or gold fillings, making resin or glass ionomer safer alternatives.
By carefully weighing these factors, patients and dentists can collaborate to choose the most suitable and effective dental fillings for cavity treatment, ensuring both function and aesthetics are maintained.
Types of Dental Fillings for Cavity Treatment
When exploring dental fillings for cavity treatment, understanding the different types available helps patients choose the best material for their needs. Each type has its own advantages, limitations, and ideal applications.
A. Amalgam Fillings
Amalgam is a silver-colored mixture of mercury, silver, tin, and copper. It’s known for its durability and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for many years. Amalgam can withstand strong chewing forces, making it ideal for molars and high-pressure chewing areas. However, its metallic appearance is easily noticeable, and concerns have been raised over its mercury content, though it remains widely used and deemed safe by dental associations.
B. Composite Resin Fillings
These are tooth-colored fillings made from a mixture of plastic and fine glass particles. Composite resin blends naturally with surrounding teeth and requires less drilling, preserving more tooth structure. While they offer excellent aesthetics, they are less durable than amalgam and may wear or stain over time. Composite fillings are best suited for front teeth or small to mid-sized cavities.
C. Ceramic Fillings (Porcelain)
Ceramic fillings are crafted from high-quality porcelain, offering natural tooth-like color and excellent stain resistance. They’re ideal for those seeking a strong, aesthetic solution, especially for visible areas. However, they are more expensive and usually require multiple visits, especially when used as inlays or onlays. Ceramic is great for patients prioritizing aesthetics and strength.
D. Glass Ionomer Fillings
Made from acrylic and a specific type of glass, these fillings release fluoride, offering additional protection against decay. They are ideal for children, especially for baby teeth or non-load-bearing areas. However, they are less durable and aesthetic, making them unsuitable for high-pressure or highly visible areas.
E. Gold Fillings
Gold fillings are the most durable option, lasting decades with proper care. They are biocompatible and well-tolerated by gum tissues. However, gold is visibly distinct, very expensive, and requires multiple appointments. These are ideal for patients valuing longevity over aesthetics.
Each option for dental fillings for cavity treatment offers unique benefits tailored to specific oral health and cosmetic needs.
Comparing the Types of Fillings
When considering dental fillings for cavity treatment, comparing the various options based on key attributes can help in making an informed choice. Below is a detailed comparison of the most common filling types:
Comparison of Dental Fillings for Cavity Treatment
| Filling Type | Aesthetics | Longevity | Cost | Strength | Ideal Placement | Biocompatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amalgam | Low (silver-colored) | 10–15 years or more | Low | Very strong | Back teeth, molars | Generally good, mercury debated |
| Composite Resin | High (tooth-colored) | 5–10 years | Moderate | Moderate | Front teeth, small to mid cavities | Good |
| Ceramic (Porcelain) | Excellent | 10–15 years or more | High | Strong | Visible areas, inlays/onlays | Excellent |
| Glass Ionomer | Moderate (opaque) | 3–7 years | Low to moderate | Low to moderate | Baby teeth, non-load-bearing | Very good (fluoride-releasing) |
| Gold | Low (metallic) | 15–30+ years | Very high | Very strong | Molars, long-lasting restorations | Excellent |
Each filling type used in dental fillings for cavity treatment offers a balance between aesthetics, function, and cost. Composite and ceramic are ideal for patients concerned with appearance, while amalgam and gold offer superior durability. Glass ionomer is particularly useful in pediatric or preventive dentistry. Ultimately, the right choice depends on individual needs, placement location, and dental professional guidance.
How to Choose the Right Dental Filling for Cavity Treatment
Choosing the right material for dental fillings for cavity treatment involves more than simply filling a cavity—it’s about making a decision that aligns with your oral health needs, aesthetic goals, and lifestyle. The best way to begin is with a consultation with your dentist, who will assess the location, size, and severity of the cavity, along with your dental history, to recommend suitable options.
Personal priorities also play a significant role. If maintaining a natural look is important, composite resin or ceramic fillings may be preferred for their tooth-colored appearance. On the other hand, if function and durability are your main concerns, especially for molars or hard-to-reach areas, amalgam or gold fillings might be more appropriate.
Your lifestyle and budget are additional factors to consider. Gold and ceramic fillings offer exceptional longevity but come at a higher cost. Composite and amalgam are more affordable and commonly covered by insurance. People with active lifestyles or heavy teeth grinders may benefit from stronger materials like gold or amalgam.
Lastly, think about your long-term oral health goals. If you’re prone to cavities, fluoride-releasing materials like glass ionomer can provide added protection. Patients interested in holistic dentistry may prioritize biocompatibility and choose non-metallic options.
Making the right decision about dental fillings for cavity treatment ensures comfort, function, and lasting results tailored to your individual needs.
Caring for Your Fillings
Proper care is essential to extend the life of dental fillings for cavity treatment and maintain overall oral health. Begin with consistent oral hygiene practices—brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to prevent plaque buildup around the fillings. Regular dental check-ups every six months help detect any issues early.
Avoid hard or sticky foods, especially in the days following the placement of your dental filling. Biting on ice, chewing hard candies, or eating caramel can damage or dislodge the filling. This is particularly important for materials like composite resin or glass ionomer, which may be more prone to wear or cracking under pressure.
Stay alert to warning signs that indicate your filling may need attention. Contact your dentist if you experience sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods, feel a sharp edge with your tongue, notice a crack or chip, or if the filling becomes loose. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to further decay or infection.
With proper care, dental fillings for cavity treatment can last many years while keeping your smile healthy, functional, and pain-free. Prevention and regular monitoring are key to maximizing the effectiveness of your treatment.
Conclusion
In summary, various dental fillings for cavity treatment—including amalgam, composite resin, ceramic, glass ionomer, and gold—offer unique benefits based on durability, aesthetics, and cost. Choosing the right filling depends on individual needs, and professional guidance is essential to make an informed decision. Dentists evaluate each case to recommend the most suitable option for lasting results. Regular dental visits not only help monitor existing fillings but also aid in early cavity detection and prevention. By staying proactive with oral care and routine check-ups, you can protect your smile and ensure the long-term success of your dental treatments.